Heimildir
Heimildir
Co-enzym Q10 |
| Synonymer | Q10 \ Ubikinon |
Barn | Ĺldersintervall | Referensintervall |
| | <17 ĺr | 0,30 - 1,5 |
Vuxna | Ĺldersintervall | Referensintervall |
| | >=17 ĺr | 0,55 - 1,8 |
| Remiss | Remiss 2 Metabolism | System | Plasma |
| Remissord | P-Q10 |
| Provtagning och hantering | 5 mL K3-EDTA |
Helst fasteprov och tidigast 12 timmar efter senaste dos
Remissen kan hämtas pĺ hemsidan: www.kliniskkemi.se
Provet centrifugeras plasman avskiljes Skyddas för ljus Förvaras kylt.
|
| Metod | HPLC-EC |
| Storhet | Substansmängdskoncentration | Enhet | µmol/L |
| NPU-Kod | Saknas | Ackrediterad | Nej |
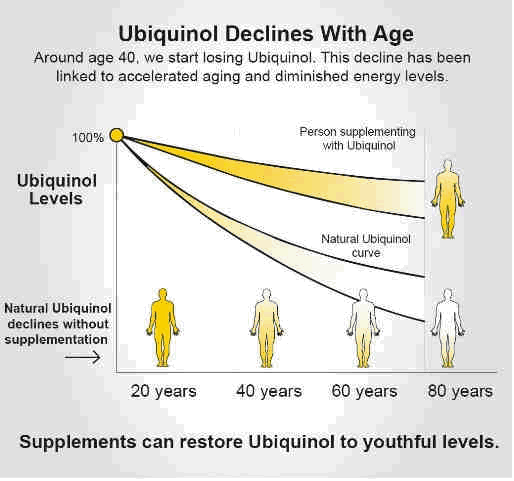
Fróđleikur: Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) is a vitamin-like nutrient that is found embedded in the mitochondria in our cells. As part of the energy making process, CoQ10 acts to shuttle electrons through a series of reactions, culminating in the production of the energy molecule adenosine tri-phosphate (ATP) – upon which all cellular functions in the body depend. As CoQ10 accepts electrons, it becomes ‘reduced’ (to ubiquinol) and as it gives up electrons, it becomes ‘oxidised’ (to ubiquinone). As long as the body is fuelled with CoQ10 through our diet, and CoQ10 is present in our cells, it’s a perpetual energy process that sustains us. If, however, Physical and Mental Fatigue CoQ10 levels become depleted, the production of ATP is significantly affected. For many people, low energy and fatigue may simply be a symptom of CoQ10 deficiency.
CoQ10 is vital to the production of energy in the body. A deficiency can cause extreme physical fatigue. People with low levels of this enzyme may feel tired upon waking, or exhausted after just a few minutes of walking. Low CoQ10 levels can also cause mental fatigue. Symptoms include difficulty concentrating and memory lapses. People will also experience mood changes such a loss of enthusiasm, mild to moderate depression, irritability and a decreased ability to handle stress, according Dr. Jacob Teitelbaum, medical director of the Fibromyalgia and Fatigue Centers.
Chronic Pain Low ATP production is linked to increased pain. People deficient in CoQ10 often experience frequent headaches, migraines, jaw pain, or muscle and joint aches. There is also an increased risk of developing fibromyalgia, a chronic condition marked by widespread pain and extreme sensitivity to touch.
Weak Immune System A weak immune system is also associated with low levels of CoQ10. People with this deficiency are more susceptible to cold and flu viruses, and they often suffer with chronic gum infections, says Dr. Teitelbaum. Without sufficient energy, the body cannot produce sufficient protective antibodies and defenders like the T-cells and macrophages cannot carry out their germ-fighting functions properly, he adds.
Increased Risk of Heart Disease and Obesity Low levels of CoQ10 causes inflammation that leads to high blood pressure and high cholesterol, raising the risk heart disease, according to research published in the December 2009 issue of "Pharmacology and Therapeutics." A CoQ10 deficiency also reduces energy in cardiac cells, increasing the risk of heart failure.Some studies have found that CoQ10 levels are 52 percent lower in obese people, leading some researchers to believe that low levels are a factor in weight gain and difficulty shedding excess pounds.
Neurological Disorders Low levels of CoQ10 are also linked with a number of neuromuscular and neurodegenerative disorders, including myalgic encephalomyelitis, Parkinson's disease, Huntington's disease and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.