Samheiti: Trypsinogen (ensym)
 Heimildir
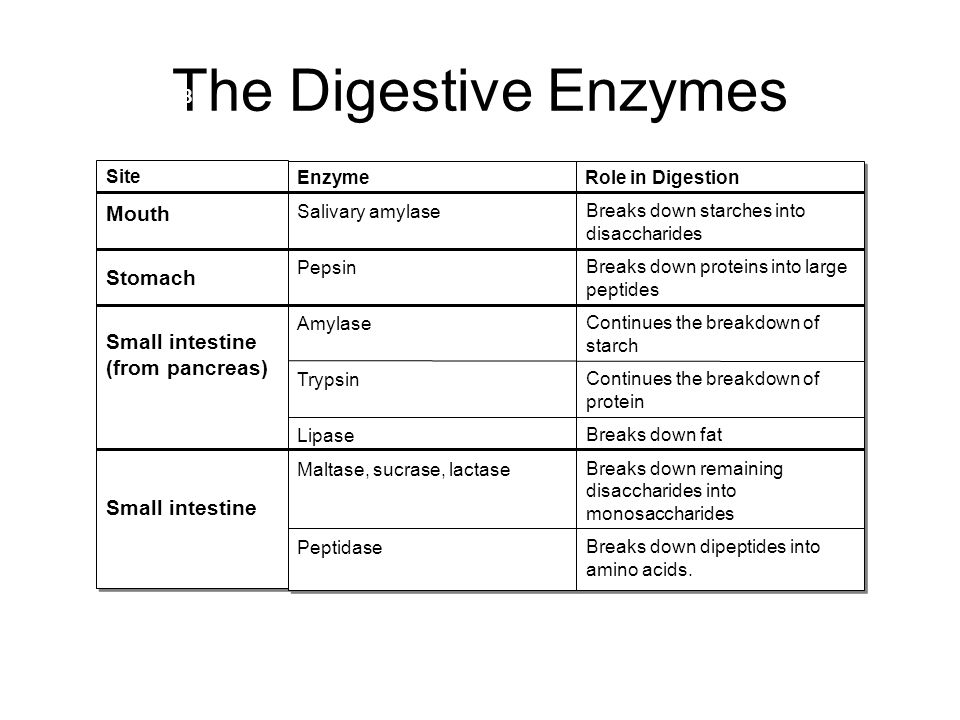
Trypsin
Heimildir
Trypsin
| Synonyme | Immunogenes trypsinogen |
| Kategorien | Pankreatitis |
| Material | 1 ml Serum |
| Probentransport | Kurierdienst |
| Ansatztage | 1-2/Woche |
| Richtwerte |
| Alter | µg/l |
| < 2 Jahre | 60 - 320 |
| 2 - < 14 Jahre | 45 - 345 |
| 14 - < 40 Jahre | 140 - 450 |
| 40 - < 60 Jahre | 140 - 500 |
| >= 60 Jahre | 140 - 600 |
|
| Methode | Radio-Immunoassay (RIA) |
| Klinische Indikation | Diagnose und Verlaufsbeurteilung der Pankreatitis, Pankreasfibrose, Pankreaskarzinom, Neugeborenen-Screening (3. - 5. Lebenstag) |
| Beurteilung | Trypsin im Serum ist erhöht bei Pankreasaffektionen. Zur Beurteilung einer Prankreatitis sind Marker wie Lipase, Pankreas-Amylase und Pankreas-Elastase 1 im Serum aussagekräftiger. Erhöhte Werte im Neugeborenen-Screening müssen mittels Schweiß-Test abgeklärt werden. Erhöhte Werte können auch bei gestörter Nierenfunktion auftreten. |
| Durchführung | Eigenleistung |
| Akkreditiert | ja |
| Stand | 2019-06-03 |
Fróđleikur:
Trypsin is a serine protease from the PA clan superfamily, found in the digestive system of many vertebrates, where it hydrolyses proteins.[2][3] Trypsin is formed in the small intestine when its proenzyme form, the trypsinogen produced by the pancreas, is activated. Trypsin cleaves peptide chains mainly at the carboxyl side of the amino acids lysine or arginine, except when either is followed by proline.[4] It is used for numerous biotechnological processes.
In the duodenum, trypsin catalyzes the hydrolysis of peptide bonds, breaking down proteins into smaller peptides. The peptide products are then further hydrolyzed into amino acids via other proteases, rendering them available for absorption into the blood stream. Tryptic digestion is a necessary step in protein absorption as proteins are generally too large to be absorbed through the lining of the small intestine.[7]